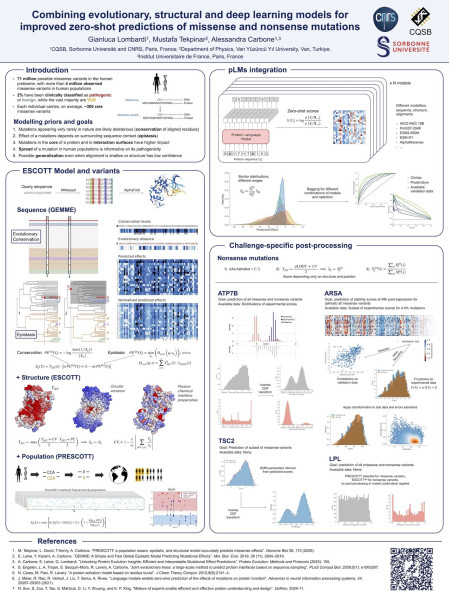
PRESCOTT, combined with state-of-the-art Deep Learning models, has been invited to the “Distinctive Advances in Missense Prediction” session of the prestigious CAGI7 (Critical Assessment of Genome Interpretation) challenge. This invitation highlights the growing impact of PRESCOTT in predicting the functional effects of missense mutations across diverse biological systems.
Gianluca Lombardi (PhD doctorant at SCAI) will be in Boston to present PRESCOTT and its Deep Learning extensions, showcasing results on four major CAGI7 challenges, each focused on assessing the consequences of genetic variants:
1. Arylsulfatase A (ARSA)
Prediction of protein-stability changes in ARSA, an enzyme involved in metachromatic leukodystrophy (MLD), an autosomal recessive lysosomal-storage disorder.
2. Lipoprotein Lipase (LPL)
Evaluation of the impact of LPL variants using a surface-abundance assay in mammalian cells, critical for understanding lipid-metabolism regulation.
3. Tuberin (TSC2)
Assessment of TSC2 protein stability, a tumor suppressor that plays a central role in the regulation of cell growth and proliferation.
4. Copper-Transporting ATPase 2 (ATP7B)
Prediction of functional effects of ATP7B variants based on a yeast-growth assay, relevant for deciphering copper-transport dysregulation, including mechanisms associated with Wilson disease.
Alongside the invited talk, Gianluca Lombardi will present a poster summarizing the results obtained on the four CAGI7 challenges, detailing methodology, predictive performance, and the added value of combining PRESCOTT with Deep Learning strategies.